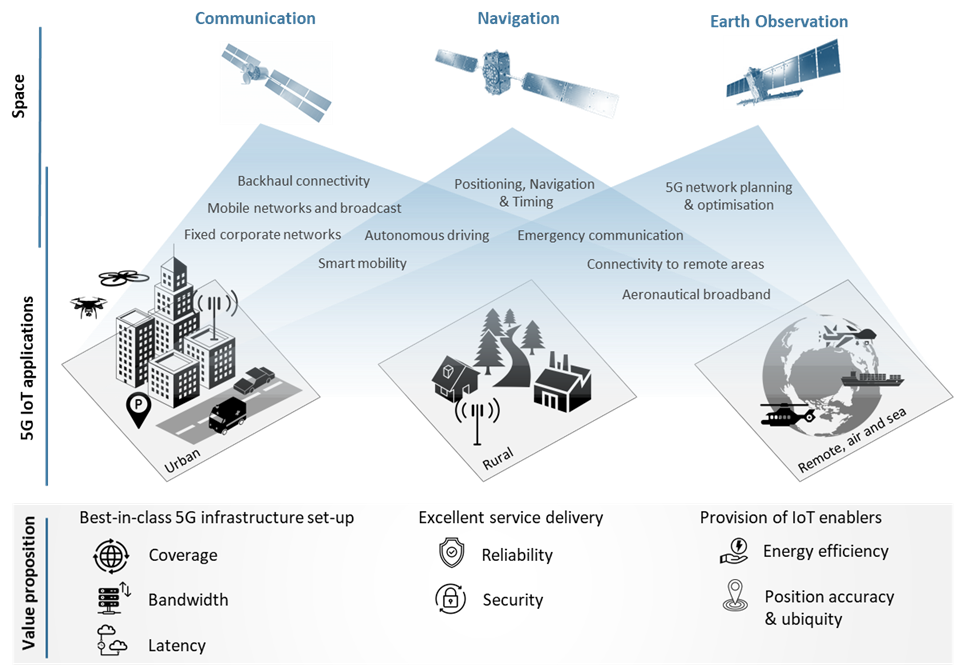
Space can pave the way towards accelerating a sustainable and inclusive transition to 5G networks, creating significant economic and social value in the European economy[1]. Space technologies have endless touchpoints with IoT, be it providing ubiquitous connectivity and enhanced capacity with the help of Satellite Communication, geospatial data to plan and optimise 5G networks with the help of Earth Observation, or high-accuracy positioning with the help of Satellite Navigation.
Will the next space race be 5G-enabled satellites?
5G-enabled LEO satellites work with terrestrial 5G infrastructure to extend 5G networks across sea, air and other remote areas. This improves the experience quality[2] of high capacity applications, saves valuable spectrum, and improves the resilience of each network. Billions of future 5G IoT devices will need constant updates that require an efficient distribution of data on a global scale. Satellite communication is well-positioned to support IoT by offering shared uplink connectivity, data aggregation and additional capacity as an IoT backup, amongst others, thus permitting higher peak rates and more reliability in massive machine communication[3]. LEO based communication networks may play a part on the road to 6G as well[4].
The increased complexity of 5G network planning requires state-of-the-art geospatial data
5G network planning is much more complex compared to previous generations. The network of cell sites has to be densified through microcells and be well geospatially planned. This is due to the fact that the signal is more susceptible to issues such as topography diversity, vegetation density, building materials, and other factors. In addition, existing capacity must be mapped and networks must be flexibly designed to meet user requirements from emerging applications and use cases. As a result, geospatial data is crucial to achieving a best-in-class infrastructure set-up, subsequently enhancing coverage, bandwidth, latency and reliability as well as ensuring excellent service delivery. Geospatial data provides insights for decision-making in 5G/6G infrastructure deployment and network planning and enhances downstream IoT applications in many industry verticals.
5G enabled IoT applications benefit from satellite navigation
As the trend shifts from stationary to moving interconnected devices, many applications require or benefit from location information. Location-aware IoT devices that are connected to the internet via 5G can be found in several industry verticals. Low-power GNSS technologies[5] enable positioning fit for IoT by combining accuracy and ubiquity. This provides high accuracy on a large scale that is independent of the ground infrastructure network[6]. 5G and SatNav integrated solutions enhance the positioning capabilities of IoT devices, enabling a wide range of applications and services such as autonomous driving, high-precision drones, smart cities and Industrial IoT[7].
5G offers unprecedented business opportunities for the European space sector
5G is the first generation to see space technologies incorporated from the get-go. This allows satellite operators, service providers and manufacturers across Europe to break out of their niche and deliver a significant part of the future generation of communications, networks, and services. 5G brings together the traditional space sector, the telecommunication sector and many other verticals[8]. The business potential of LEO constellations to deliver high-speed internet is broadly recognised, in particular by the likes of SpaceX and Amazon, expecting considerable revenue opportunities to open up. The same players are looking into related business models such as enabling cloud data traffic via satellite or making data from space more accessible by leveraging its cloud capabilities bringing companies closer to the edge[9]. Nonetheless, there remain many operational, technical and regulatory challenges related to the development of integrated space-terrestrial communication networks. The viability and sustainability of these emerging business models are still to be proven. For instance, while integrating 5G with LEO SatComs has become a trending topic, none of them have actually achieved full 5G compatibility[10].
Space and the 5G IoT value proposition
5G is expected to revolutionise the way we live by spurring countless new applications. 5G was developed with the main purpose of enabling IoT use cases. The role of space within the 5G IoT value proposition is twofold:
- The integration of satellite access together with terrestrial 5G networks and the use of geospatial data for 5G network planning and optimisation will bring 5G networks to the performance level needed for future IoT applications. This is true for coverage, quality of experience and other key performance indicators.
- Integrating 5G and space technologies into IoT applications will enhance their performance and will thus play a part in reshaping various vertical domains such as eHealth, energy, smart city and agriculture to name only a few. For instance, communication capabilities of current cellular networks are already used routinely to supplement satnav-based smartphone positioning performance.
While integrating these revolutionising technologies into solutions that bring added value to the end user offer many business opportunities and open the doors for new industry corporation, it comes with many technical and commercial challenges. Businesses may need to rely on strategic advice to navigate the transformation caused by the advent of 5G and how space technologies enable them.
[1] European Union Member States and the United Kingdom
[2] The Quality of Experience is a set of measurements to verify network quality providing detailed indicators to diagnose issues and to optimise performance
[3] Nokia Real Insights, 5G from space – The role of satellites in 5G
[4] Lin et al., On the Path to 6G: Low Orbit is the New High, 2021
[5] Point.MOOC, How does positioning work for the Internet of Things?, a training developed by Novaspace in a Horizon 2020 funded project by the European Commission
[6] ESA 5G GNSS Task Force: The role of GNSS in 5G wireless networks, InsideGNSS, November 2019
[7] ESA Applications ”5G to help smart factories and masses of drones find their way”, November 2020
[8] ESA “Space for 5G and 6G” Strategic Programme under its ARTES 4.0 programme
[9] Northern Sky Research (NSR), Cloud Computing via Satellite, 2nd Edition, June 2021
[10] Liu et al., LEO Satellite Constellations for 5G and Beyond: How Will They Reshape Vertical Domains?, 2021